Underground Mining Environmental Impact: Understanding Risks and Solutions
Mining has been an essential part of human progress for thousands of years. From the gold rushes of the 1800s to today’s high-tech industrial operations, mining provides us with the minerals and metals that power everything from smartphones to skyscrapers. However, while mining brings economic benefits, it also has environmental costs. Among the various mining methods, underground mining is often seen as less destructive than open-pit mining, yet it still has significant environmental impacts that need attention.
In this article, we will explore the underground mining environmental impact, breaking it down into understandable sections, sharing real-world anecdotes, and giving step-by-step insights on how these impacts can be minimized.
What is Underground Mining?
Underground mining involves extracting minerals and metals from deep beneath the Earth’s surface. Unlike surface mining, which removes large areas of soil and rock, underground mining focuses on creating tunnels and shafts to reach the desired deposits.
Some common underground mining techniques include:
-
Room-and-Pillar Mining: Large chambers are created underground, leaving pillars of rock to support the roof.
-
Longwall Mining: Entire horizontal sections of ore are removed using mechanized equipment, allowing the roof to collapse behind the operation safely.
-
Block Caving: Gravity is used to break ore, allowing it to collapse and be collected.
While these methods reduce surface disturbance, they are not without environmental consequences.
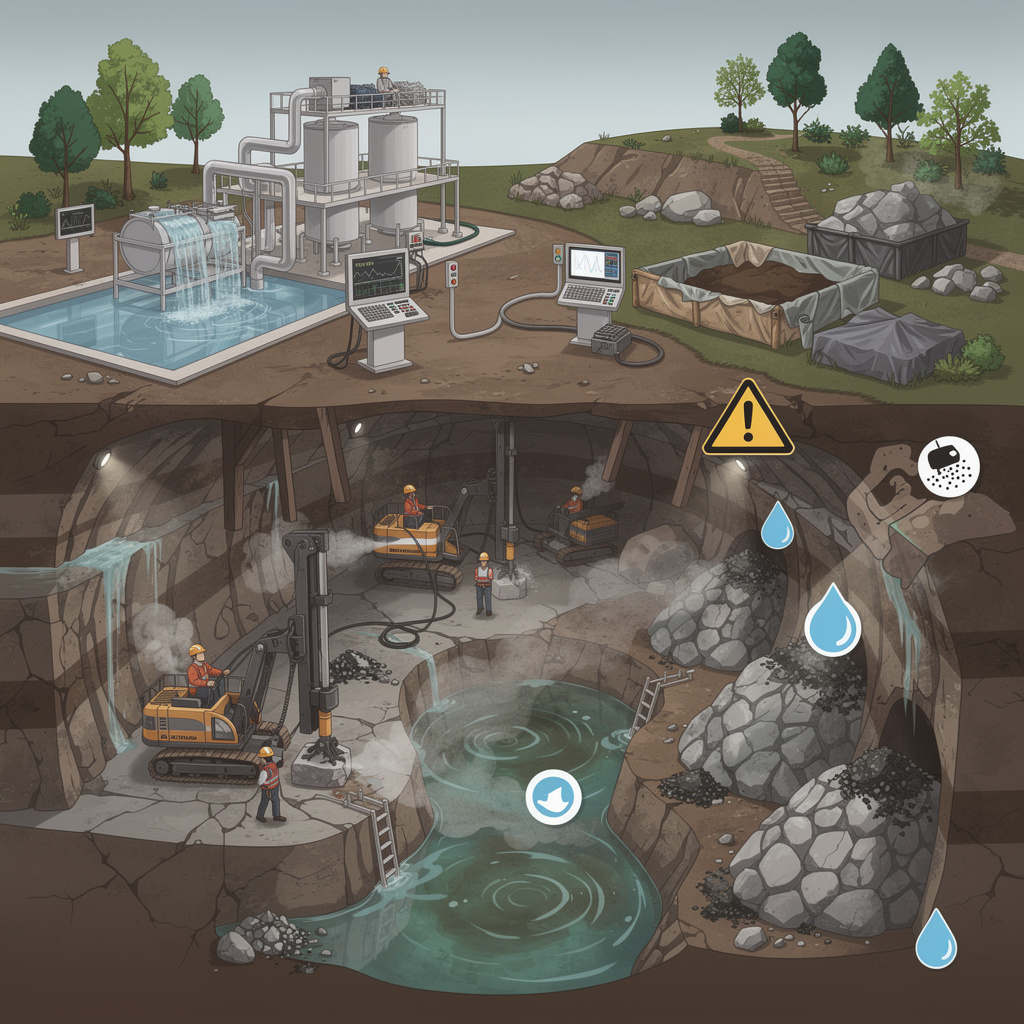
Major Environmental Concerns in Underground Mining
Even though underground mining is less visible than open-pit mining, it affects ecosystems, water resources, and air quality. Let’s take a closer look.
1. Water Pollution
Water is vital, yet mining operations often use large amounts of it for drilling, cooling equipment, and processing minerals. Contaminated water can be a major issue.
A real-world example: In certain coal mines in the Appalachian region of the United States, acid mine drainage (AMD) occurs when sulfide minerals react with water and air, forming sulfuric acid that contaminates nearby rivers. This not only harms aquatic life but also affects communities relying on these water sources.
Step-by-step water management in underground mining:
-
Source Control: Identify water sources that could be contaminated.
-
Treatment: Use filtration systems and neutralization techniques to treat mine water.
-
Recycling: Reuse water in operations instead of discharging it.
-
Monitoring: Regularly test water quality in surrounding areas.
By following these steps, mining companies can significantly reduce water contamination risks.
2. Soil Degradation
When underground tunnels are excavated, soil above and around the mined areas can become unstable. Over time, subsidence can occur, causing the land to sink. This can disrupt farming, housing, and local vegetation.
Example anecdote: A mining town in Australia noticed cracks appearing in roads and local farmland after years of underground gold mining. Engineers worked with the mining company to stabilize the tunnels and restore land integrity.
Mitigation steps for soil protection:
-
Reinforce underground tunnels with supports.
-
Monitor areas above mines for signs of subsidence.
-
Rehabilitate land after mining by reshaping the terrain and planting native vegetation.
3. Air Quality Concerns
Underground mining can release dust and gases, including methane, which affect air quality. Poor ventilation can put miners and nearby communities at risk.
Step-by-step air quality management:
-
Ventilation Systems: Install effective airflow systems to disperse harmful gases.
-
Dust Suppression: Use water sprays or chemical dust suppressants.
-
Emission Control: Replace diesel equipment with electric or hybrid machinery.
-
Monitoring: Track air quality regularly to detect hazards early.
This reduces health risks and contributes to safer mining operations.
4. Impact on Biodiversity
Even underground operations can disturb ecosystems. Ventilation shafts, roads, and access tunnels fragment habitats, affecting wildlife movement.
Example: In Queensland, Australia, mining companies created buffer zones around critical habitats and wildlife corridors, allowing species to move safely while mining continued.
Best practices to protect biodiversity:
-
Conduct environmental impact assessments (EIAs) before starting mining.
-
Avoid mining in sensitive ecological areas.
-
Create habitat corridors and buffer zones.
-
Reintroduce native species during land rehabilitation.
5. Waste Management and Tailings
Mining generates waste materials called tailings, which contain leftover minerals and chemicals. Improper disposal can cause long-term contamination of soil and water.
Step-by-step approach to safe waste management:
-
Reprocessing Tailings: Extract additional minerals from waste before disposal.
-
Dry Stack Tailings: Compress tailings into solid form to prevent leaks.
-
Containment Systems: Use secure structures to prevent toxic material from reaching the environment.
Innovations Reducing Underground Mining Environmental Impact
Technology has transformed underground mining, making it more environmentally responsible:
-
Electric Mining Vehicles: Reduce carbon emissions from diesel engines.
-
Automation and AI: Improve excavation precision, reducing waste.
-
Remote Monitoring: Sensors and drones track soil, water, and air quality in real-time.
-
Predictive Modeling: Anticipates subsidence, water contamination, and other risks before they occur.
Land Rehabilitation: Restoring Ecosystems After Mining
After mining concludes, land rehabilitation is crucial to restoring ecosystems. Activities may include:
-
Refilling mine shafts.
-
Re-contouring the landscape.
-
Replanting native vegetation.
-
Creating wetlands or wildlife habitats to replace what was lost.
Step-by-step rehabilitation process:
-
Assess the Land: Identify areas damaged during mining.
-
Plan Rehabilitation: Design a restoration plan including vegetation, water management, and erosion control.
-
Implement: Carry out land reshaping, soil replacement, and planting.
-
Monitor: Track ecosystem recovery and adjust strategies as needed.
Regulations Driving Sustainable Mining Practices
Underground mining is regulated to reduce environmental impact. Key frameworks include:
-
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Identify risks before mining begins.
-
National Mining Codes: Regulate waste disposal, emissions, and land restoration.
-
International Guidelines: Organizations like the International Council on Mining and Metals (ICMM) provide sustainable mining standards.
Compliance ensures that companies prioritize both economic goals and environmental responsibility.
A Global Perspective: Lessons from Australia
Australia is a world leader in sustainable mining. Companies follow strict regulations like the Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act to manage:
-
Water conservation
-
Waste and tailings disposal
-
Air quality
-
Land rehabilitation
Real-life success story: At South32’s Cannington mine in Queensland, water recycling initiatives reduced freshwater use by 60%, demonstrating how underground mining can be conducted responsibly.
Conclusion: Balancing Mining and the Environment
Mining is vital for human development, but its environmental impact cannot be ignored. Underground mining environmental impact—including water pollution, soil degradation, air quality issues, and biodiversity loss—requires careful planning, technology adoption, and regulatory compliance.
By adopting energy-efficient equipment, responsible waste management, water conservation strategies, and robust land rehabilitation programs, mining companies can reduce environmental harm while still providing essential resources.
The key is balance: ensuring that mining activities meet human needs today without compromising the health of ecosystems for tomorrow.
FAQs on Underground Mining Environmental Impact
-
How does underground mining affect water sources?
Contaminants can leak into rivers and groundwater; recycling and treatment systems help reduce this risk. -
What causes soil degradation in underground mining?
Tunnel excavation and subsidence destabilize the land, affecting agriculture and vegetation. -
How can air quality be protected in underground mining?
Through ventilation systems, dust suppression, and electric or hybrid machinery. -
Why is biodiversity at risk in underground mining?
Infrastructure like shafts and roads fragment habitats, disturbing wildlife movement. -
How can waste from underground mining be managed safely?
Tailings can be reprocessed, stored in dry stacks, and securely contained to prevent pollution.










One Response
Что такое XCARDS — платформу, которая меня заинтересовала.
Недавно наткнулся про новый бренд XCARDS,
который предлагает создавать электронные платёжные карты чтобы
контролировать расходы.
Что обещают:
Первая карта оформляется примерно за считанные минуты.
Пользователь может создать множество карт для разных целей.
Есть поддержка круглосуточно включая живое общение с оператором.
Все операции отображаются онлайн
— лимиты, уведомления, отчёты, статистика.
Возможные нюансы:
Юрисдикция: офшорная зона — перед использованием
стоит убедиться, что сервис
можно использовать без нарушений.
Финансовые условия: в некоторых случаях встречаются скрытые комиссии, поэтому лучше внимательно изучить договор.
Практический опыт: по отзывам вопросы
решаются оперативно.
Безопасность: сайт использует шифрование, но всегда лучше не хранить большие суммы на карте.
Итоги:
Судя по функционалу, XCARDS может стать
современным решением в области рекламы.
Он объединяет интуитивный контроль и
моментальный выпуск карт.
Интересно услышать опыт других
Пробовали ли подобные сервисы?
Расскажите, как у вас работает Виртуальные карты
для онлайн-платежей https://baoly.ru/153