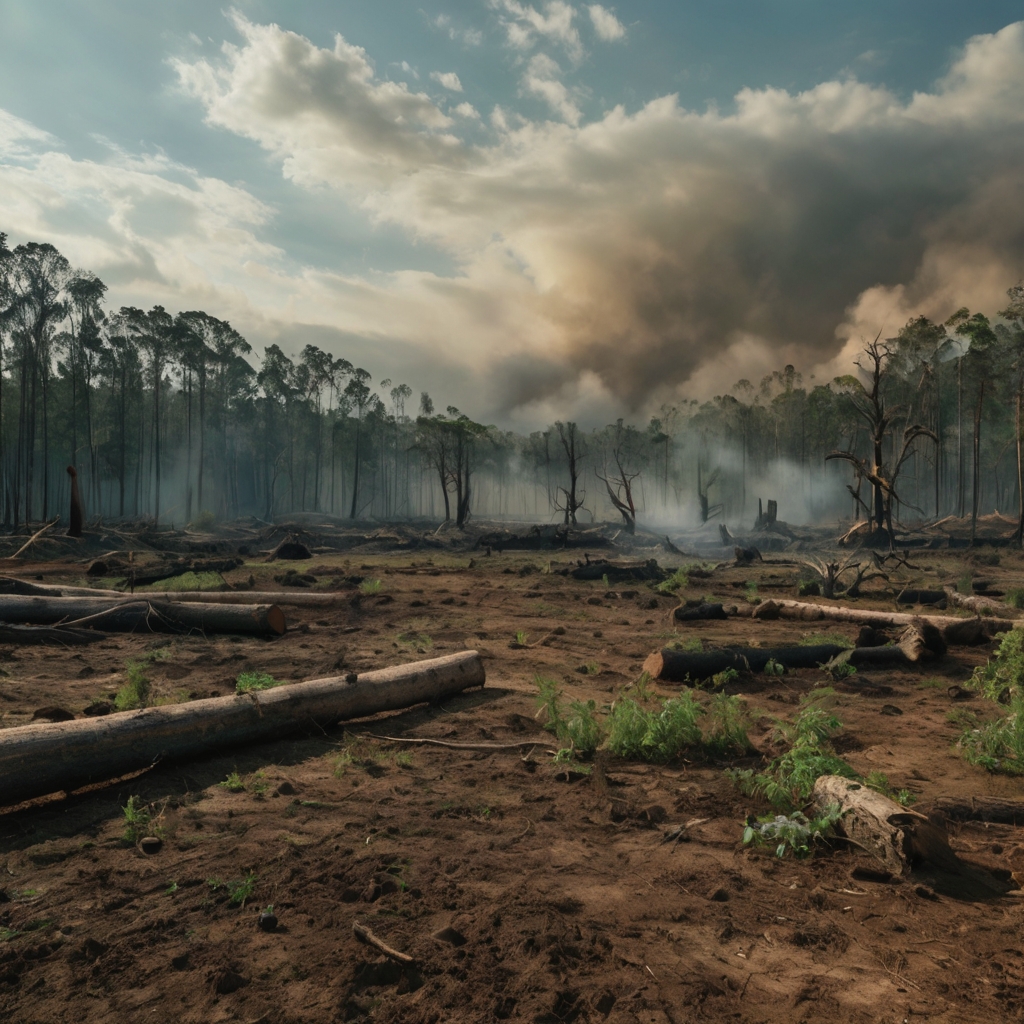
What is Deforestation and Why It Matters
Deforestation impacts the environment in more ways than many realize. It involves the clearing or thinning of forests, often to make way for agriculture, infrastructure, or logging. While this may provide short-term economic gain, the long-term environmental costs are steep. Forests are essential for clean air, climate stability, water cycles, and biodiversity. When trees are cut down at a rapid rate, it disrupts these natural processes and sets off a chain of environmental consequences that can affect ecosystems and human life globally.
Causes Behind Widespread Tree Loss
Understanding what drives deforestation helps us tackle the problem at its roots. One of the main causes is agriculture. Farmers clear forests to create more land for crops and livestock. Industrial logging is another major factor—wood is harvested for construction, paper, and fuel. Urban expansion plays a growing role, especially in developing regions. Additionally, mining and infrastructure projects like roads and dams require large-scale land clearing. Each of these activities contributes to the ongoing loss of forest cover worldwide, with ripple effects on the environment.
The Role Forests Play in a Healthy Ecosystem
Forests are often called the lungs of the Earth—and for good reason. They absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping regulate the planet’s climate. Trees also help stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. Forest ecosystems support more than 80% of the world’s terrestrial species, making them hotspots for biodiversity. They also influence rainfall patterns and maintain the water cycle, which is crucial for farming and freshwater resources. In short, forests are central to both ecological health and human survival.
Climate Change and the Carbon Cycle
One of the most alarming ways deforestation impacts the environment is through climate change. Trees store large amounts of carbon. When forests are cut down or burned, that carbon is released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide—a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. Without enough trees to absorb CO₂, the Earth’s temperature rises. Deforestation alone accounts for nearly 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This disrupts the carbon cycle and accelerates climate-related disasters such as floods, droughts, and wildfires.
Biodiversity Loss and Wildlife Displacement
Forests are home to countless species of plants, animals, and microorganisms. When these areas are destroyed, the creatures living there lose their homes, food sources, and breeding grounds. Many species are pushed to extinction because they cannot adapt quickly enough or relocate. This loss of biodiversity reduces ecosystem resilience, making it harder for nature to recover from disturbances like disease or climate shifts. The disappearance of even one species can create a domino effect throughout an entire ecosystem.
Soil Degradation and Water Imbalance
Another serious consequence of deforestation is the degradation of soil. Without tree roots to hold the soil in place, erosion increases, and the land loses its fertility. Topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and essential for growing crops, gets washed away during heavy rains. Deforestation also disrupts natural water cycles. Trees play a key role in drawing water from the soil and releasing it into the atmosphere through transpiration. Without them, rainfall becomes irregular, rivers dry up, and droughts become more common.
Real-Life Case Studies and Global Hotspots
The Amazon Rainforest is one of the most talked-about examples of rapid deforestation. Often called the “lungs of the planet,” it has lost millions of acres to cattle ranching and soy farming. In Southeast Asia, palm oil plantations are the main culprits, pushing out native wildlife like orangutans. Even in parts of the United States, forest loss is increasing due to urban sprawl and wildfires. These real-world examples show how deforestation is not a distant problem—it’s happening across the globe with urgent consequences.
Solutions and Sustainable Alternatives
Despite the damage, there are ways to reduce deforestation and its environmental impact. One solution is reforestation, which involves planting trees in areas that were previously forested. Governments and organizations are also promoting sustainable agriculture—using farming techniques that don’t require clearing forests. Eco-friendly logging practices and stronger environmental laws can also help. On a personal level, reducing paper use, supporting sustainable products, and choosing certified wood can make a difference. These small steps add up when adopted by millions.
Why Everyone Has a Role to Play
Addressing how deforestation impacts the environment isn’t just a job for scientists or politicians—it’s something everyone can influence. By making informed choices and raising awareness, we can push for policies and practices that protect our planet’s forests. Educators can include forest conservation in curricula. Businesses can choose sustainable supply chains. Citizens can vote for leaders who prioritize the environment. Forests don’t have a voice—but we do. It’s time to speak up and act.
Final Thoughts on Deforestation’s Environmental Impact
The effects of deforestation go far beyond the loss of trees. It alters the climate, threatens biodiversity, weakens soil, and endangers future generations. But with knowledge, action, and collaboration, we can reverse the damage. Recognizing how deforestation impacts the environment is the first step toward a more sustainable world—one where forests thrive, ecosystems recover, and people live in harmony with nature.