Soil Conservation Methods: Protecting and Enhancing Our Land
Soil is the foundation of life. Without fertile soil, agriculture, food security, and even our ecosystems would suffer. Over time, soil can become degraded due to erosion, chemical contamination, overuse, and poor farming practices. That’s why soil conservation methods are critical for preserving soil health, enhancing productivity, and ensuring sustainable land use for future generations.
In this article, we will explore the most effective soil conservation methods, their benefits, challenges, and practical steps you can take to protect the land.
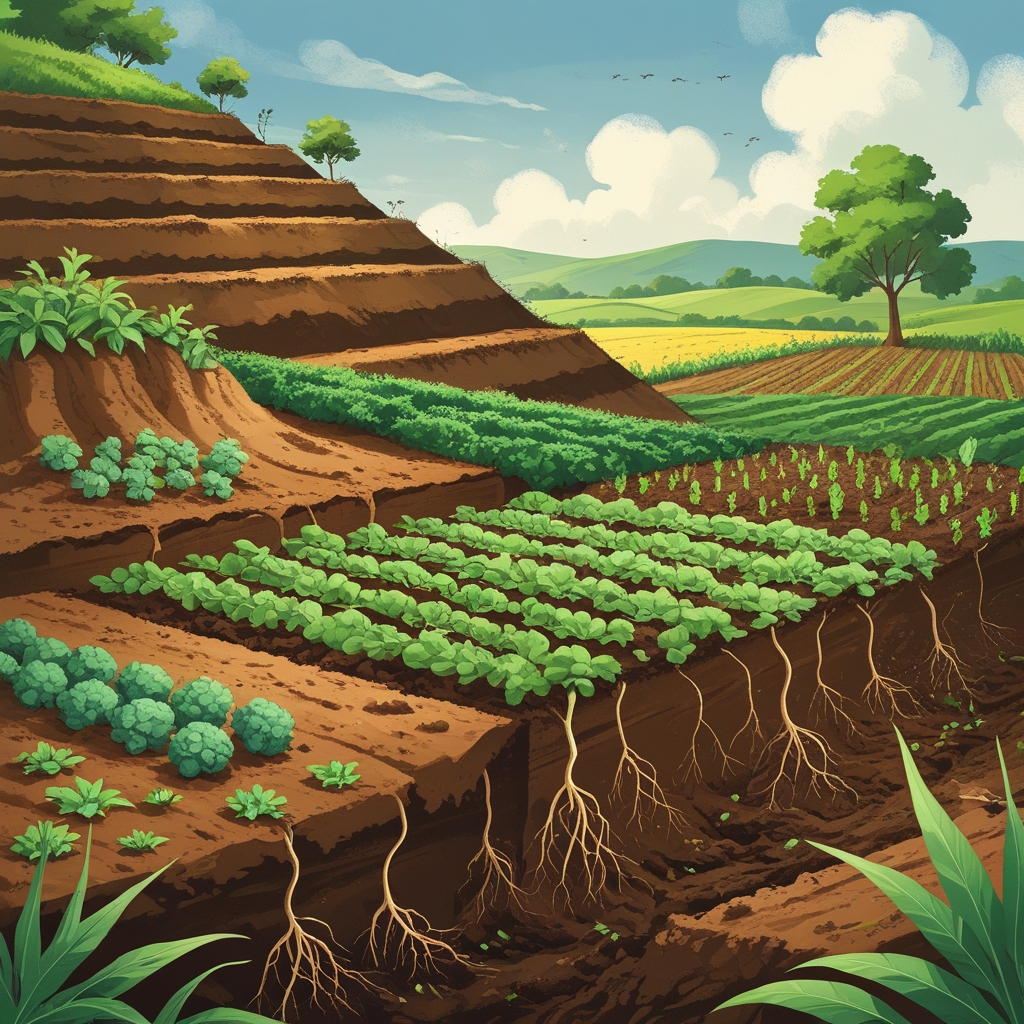
1. Soil Erosion Prevention: The First Step in Soil Conservation
Soil erosion occurs when topsoil is removed by wind, water, or human activity. This layer of soil is rich in nutrients essential for plant growth. Without it, crops struggle to grow, and rivers or lakes can become polluted with sediment.
Preventing erosion is the cornerstone of soil conservation methods. Some proven techniques include:
-
Contour farming: Planting along the natural contours of the land slows down water runoff and reduces soil loss. Learn more about contour farming.
-
Terrace farming: Creating stepped levels on slopes helps trap water and soil, reducing erosion while making steep land cultivable. Discover the benefits of terrace farming.
-
Windbreaks: Planting trees or shrubs around fields protects the soil from strong winds, especially in open plains. More on windbreaks.
Anecdote: In a rural village in California, a farmer named Miguel used to lose significant topsoil after every heavy rain. After implementing contour farming and planting windbreaks, he noticed that soil erosion reduced drastically, and crop yields improved within a single season.
2. Soil Fertility Improvement: Nurturing the Land Naturally
Soil fertility is essential for healthy crop growth. Poor soil management can deplete nutrients and organic matter. Soil conservation methods aimed at fertility improvement focus on replenishing nutrients and promoting natural soil health.
Techniques include:
-
Crop rotation: Alternating crops like legumes, cereals, and root vegetables helps restore nutrients naturally. Learn more about crop rotation benefits.
-
Cover crops: Planting crops like clover or radish between main crops prevents soil exposure, reduces erosion, and adds organic matter. Check cover crop strategies.
-
Organic soil enrichment: Using compost, green manure, and natural fertilizers improves soil structure and retains moisture. Explore organic soil enrichment.
Step-by-step tip:
-
Select a cover crop suitable for your climate and soil type.
-
Plant it immediately after harvesting your main crop.
-
Incorporate it into the soil before the next planting season to increase organic matter and nutrients.
3. Sustainable Land Management: Long-Term Soil Protection
Sustainable land management focuses on practices that maintain soil productivity over time while protecting the environment. It combines physical, biological, and chemical methods to achieve long-term conservation.
Key practices include:
-
Conservation tillage: Reduces plowing and leaves crop residues on the field, which protects the soil from wind and water erosion. Learn about conservation tillage.
-
Integrated pest management (IPM): Reduces the use of chemical pesticides, which can harm soil health and beneficial organisms. Discover IPM strategies.
-
Chemical-free farming: Avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides encourages natural soil processes and biodiversity. Explore chemical-free agriculture.
By adopting these methods, farmers can ensure that the land remains fertile, productive, and resilient to climate change.
4. Water Retention Techniques: Conserving Moisture in Soil
Water is vital for crops, but poorly managed irrigation can cause soil erosion and nutrient leaching. Water retention techniques are crucial in soil conservation methods to maintain moisture and prevent land degradation.
Techniques include:
-
Grassed waterways: Channels lined with grass reduce water speed and prevent soil washout. Read more about grassed waterways.
-
Mulching: Covers the soil surface with organic materials to reduce evaporation, suppress weeds, and improve fertility. Learn about mulching techniques.
-
Terrace systems: Captures rainwater on slopes and prevents it from washing away topsoil.
Anecdote: In India, farmers in arid regions used to lose nearly half of their rainwater to runoff. After creating simple terraces and mulching fields, they retained more water, resulting in higher yields despite a dry season.
5. Contour Farming Strategies: Farming Along Nature’s Lines
Contour farming strategies are a simple yet effective method to reduce erosion on sloped lands. By planting along the natural curves of the land, water flow slows down, and soil is retained.
Steps to implement:
-
Survey the land to determine contour lines.
-
Plant rows of crops along these contours instead of straight up and down the slope.
-
Use additional barriers like grass strips or terraces along contours for extra protection.
Tip: Combine contour farming with cover crops for maximum soil retention.
6. Crop Rotation Benefits: A Natural Way to Restore Soil Health
Crop rotation is a proven method to maintain soil fertility and prevent pests and diseases. Rotating different crops keeps the soil balanced and minimizes the need for chemical fertilizers.
Benefits include:
-
Enhanced nutrient availability in the soil.
-
Reduced risk of pests and diseases.
-
Improved soil structure and moisture retention.
Step-by-step guide:
-
Divide your fields into sections for different crops.
-
Plant nitrogen-fixing crops like beans or peas in one section, followed by cereals in the next season.
-
Monitor soil health and adjust rotations annually.
7. Windbreak Implementation: Protecting Soil from Harsh Winds
Windbreaks are rows of trees or shrubs designed to shield farmland from strong winds that can erode soil and damage crops.
Tips for effective windbreaks:
-
Plant dense evergreen species for year-round protection.
-
Position windbreaks perpendicular to prevailing winds.
-
Include multiple rows if possible, with varying heights for maximum efficiency.
Windbreaks also provide habitats for wildlife, helping maintain biodiversity. Learn more about windbreaks in agriculture.
8. Terrace Farming Advantages: Maximizing Steep Land Productivity
Terrace farming advantages include reducing runoff, preventing soil loss, and making otherwise unusable slopes productive. Terraces act as steps that slow water flow and allow it to infiltrate the soil, carrying nutrients along.
Implementation steps:
-
Identify slopes suitable for terracing.
-
Construct flat platforms step by step along the hillside.
-
Reinforce edges with stones or vegetation to prevent collapse.
-
Plant crops adapted to the terrace conditions.
Terracing is especially effective for rice paddies, vineyards, and hilly vegetable farms.
9. Integrated Pest Management in Soil Care
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) focuses on controlling pests without harming the soil ecosystem. IPM strategies include:
-
Using natural predators and beneficial insects.
-
Crop rotation to reduce pest populations.
-
Biological controls like pheromones or microbial agents.
IPM minimizes chemical input, maintaining soil fertility while protecting crops. Learn more about IPM.
10. Organic Soil Enrichment: Nature’s Way to Healthy Fields
Organic soil enrichment enhances soil fertility through natural means rather than chemicals. Methods include:
-
Composting crop residues and manure.
-
Planting green manure crops like clover to add nutrients.
-
Using microbiological fertilizers to boost soil microbial activity.
Organic enrichment improves soil structure, increases water retention, and supports beneficial organisms, leading to higher yields and healthier crops.
Conclusion: The Future of Soil Conservation Methods
Implementing soil conservation methods is not just about preserving farmland—it’s about safeguarding our food supply, protecting ecosystems, and ensuring sustainable agriculture. By using a combination of soil erosion prevention, fertility improvement, water retention techniques, and organic enrichment, farmers and landowners can maintain productive, resilient soils for generations.
Anecdote: Farmers worldwide who have adopted a mix of terraces, windbreaks, and crop rotations report increased yields, healthier crops, and a noticeable improvement in soil quality within just a few seasons.
Ultimately, soil conservation is a collective responsibility. Governments, communities, and individual farmers must work together to implement sustainable practices and maintain the health of our most critical natural resource: the soil.










One Response
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.